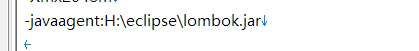第二章:lombok介绍及简单使用
一、Lombok简介
1.概述
Lombok是一个可以通过简单的注解形式来帮助我们简化消除一些必须有但显得很臃肿的Java代码的工具,通过使用对应的注解,可以在编译源码的时候生成对应的方法。
官方地址:https://projectlombok.org/ github地址:https://github.com/rzwitserloot/lombok
这里简单说下
lombok实现的原理:主要是通过抽象语法树(AST),在编译处理后,匹配到有其注解的类,那么注解编译器就会自动去匹配项目中的注解对应到在lombok语法树中的注解文件,并经过自动编译匹配来生成对应类中的getter或者setter方法,达到简化代码的目的。
利用此原理,也可自行编写一些工作中一些经常使用到的,比如实体类转Map对象,map对象转实体类,原本使用Beanutils或者cglib的BeanCopier实现转换,前者使用的是反射的机制,所以性能相对较差,后者是使用修改字节码技术,性能在未使用Converter时基本等同于set和get方法。但说白了还是麻烦,毕竟还需要缓存对象等做到复用等。
2.使用优点
- 简化冗余的JavaBean代码,使得实体文件很简洁。
- 大大提高JavaBean中方法的执行效率,省去重复的步骤
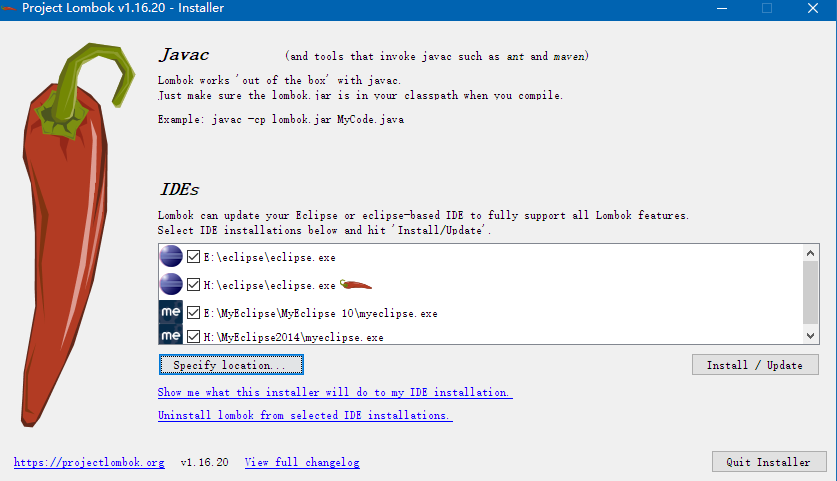
二、eclipse 安装
- 下载 lombok.jar 包
- 运行
lombok.jar包,会自动扫描系统的ide安装情况(或者手动指定目录),点击Install/Update,即可。
- 不运行jar包情况下,可直接指定
eclipse.ini文件,设置javaagent属性即可(第二种方法最后的效果也是这样的。):
三、Lombok使用
1.添加maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.16.20</version>
</dependency>
2.常用注解介绍
@Getter / @Setter:可以作用在类上和属性上,放在类上,会对所有的非静态(non-static)属性生成Getter/Setter方法,放在属性上,会对该属性生成Getter/Setter方法。并可以指定Getter/Setter方法的访问级别。@EqualsAndHashCode:默认情况下,会使用所有非瞬态(non-transient)和非静态(non-static)字段来生成equals和hascode方法,也可以指定具体使用哪些属性。 @ToString 生成toString方法,默认情况下,会输出类名、所有属性,属性会按照顺序输出,以逗号分割。@NoArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor and @AllArgsConstructor:无参构造器、部分参数构造器、全参构造器- @Data:包含@ToString, @EqualsAndHashCode, 所有属性的@Getter, 所有non-final属性的@Setter和@RequiredArgsConstructor的组合,通常情况下,基本上使用这个注解就足够了。
@Budilder:可以进行Builder方式初始化。- @Slf4j:等同于:private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(XXX.class);简直不能更爽了!一般上用在其他java类上
更多注解说明,可查看:https://projectlombok.org/features/index.html
四、简单使用示例
使用lombok
@Data
@Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Demo {
String code;
String name;
}
等同于
public class Demo {
String code;
String name;
public static DemoBuilder builder() {
return new DemoBuilder();
}
public String getCode() {
return this.code;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (!(o instanceof Demo))
return false;
Demo other = (Demo) o;
if (!other.canEqual(this))
return false;
Object this$code = getCode();
Object other$code = other.getCode();
if (this$code == null ? other$code != null : !this$code.equals(other$code))
return false;
Object this$name = getName();
Object other$name = other.getName();
return this$name == null ? other$name == null : this$name.equals(other$name);
}
protected boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return other instanceof Demo;
}
public int hashCode() {
int PRIME = 59;
int result = 1;
Object $code = getCode();
result = result * 59 + ($code == null ? 43 : $code.hashCode());
Object $name = getName();
return result * 59 + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode());
}
public String toString() {
return "Demo(code=" + getCode() + ", name=" + getName() + ")";
}
public Demo() {
}
public Demo(String code, String name) {
this.code = code;
this.name = name;
}
public static class DemoBuilder {
private String code;
private String name;
public DemoBuilder code(String code) {
this.code = code;
return this;
}
public DemoBuilder name(String name) {
this.name = name;
return this;
}
public Demo build() {
return new Demo(this.code, this.name);
}
public String toString() {
return "Demo.DemoBuilder(code=" + this.code + ", name=" + this.name + ")";
}
}
}
使用@Slf4j(摘抄至官网)
@Slf4j
public class LogExampleOther {
public static void main(String... args) {
log.error("Something else is wrong here");
}
}
常规的
public class LogExampleOther {
private static final org.slf4j.Logger log = org.slf4j.LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogExampleOther.class);
public static void main(String... args) {
log.error("Something else is wrong here");
}
}
-
转载请注明原地址https://blog.lqdev.cn/categories/springboot/
-
请关注宋德凌的博客:http://CoderOfSong.github.io 谢谢!